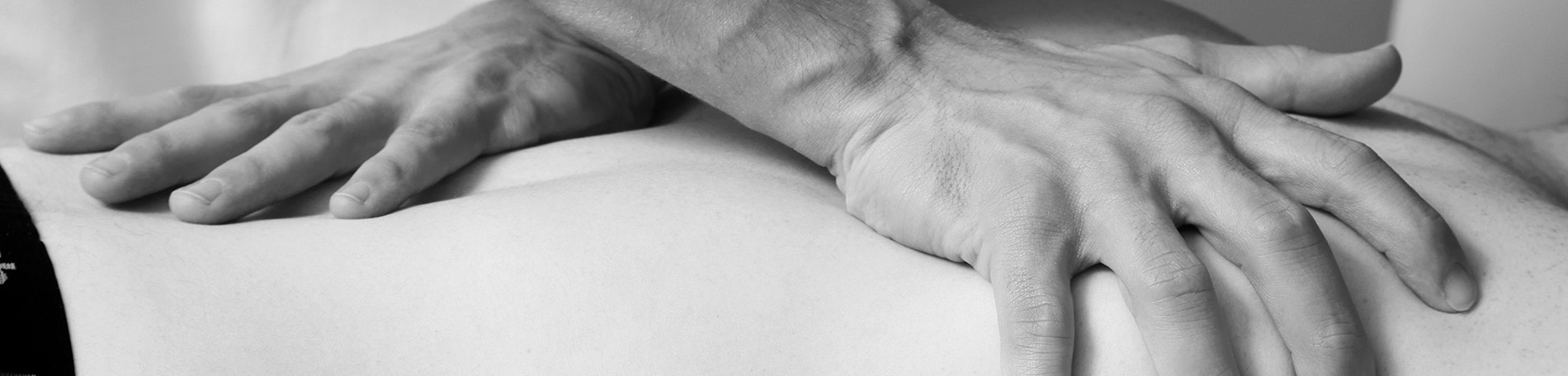
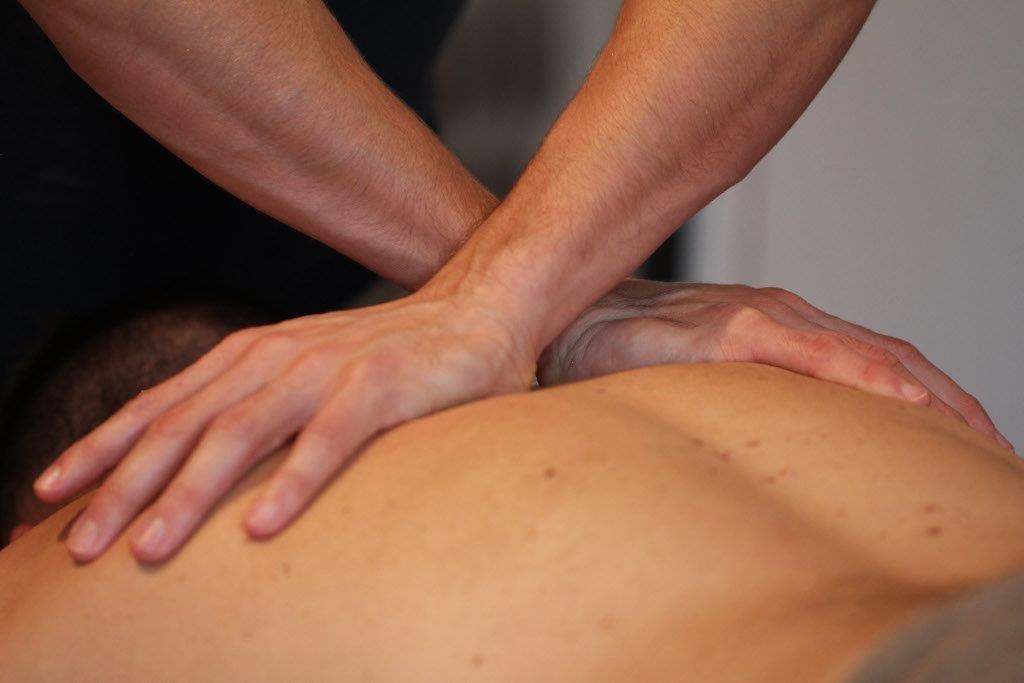
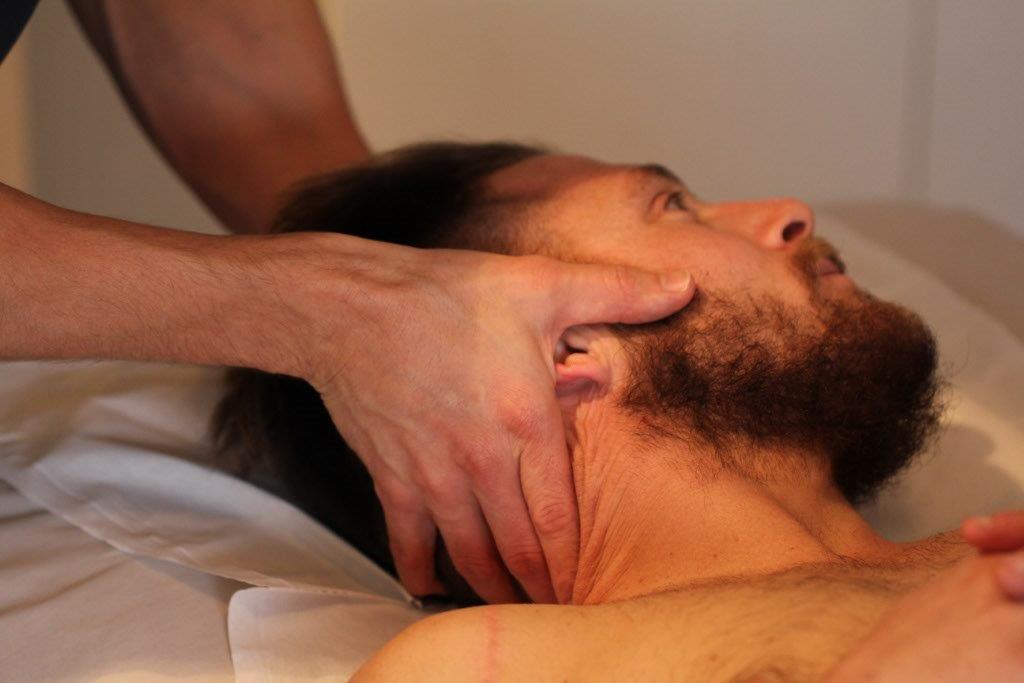
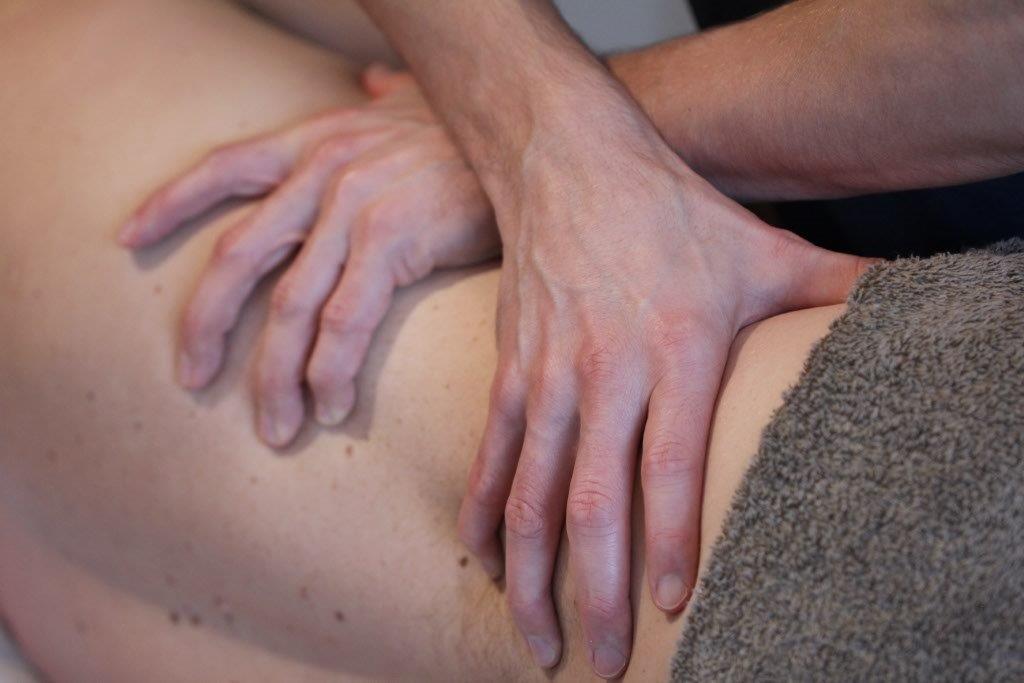
Osteopathy is a method of assessing, treating and preventing a wide range of health problems. Osteopaths use a combination of movement, stretching, targeted deep tissue massage and manipulation of a person’s muscles and joints to improve function, relieve pain and aid recovery.
The body has the natural ability to maintain itself and, by helping this process, an osteopath can promote restoration of normal function. The principle of osteopathy is that the wellbeing of an individual relies on the way that bones, muscles, ligaments, connective tissue and internal structures work with each other.
An osteopath will take the time to understand their patient, and their unique combination of symptoms, medical history and lifestyle. This helps to make an accurate diagnosis of the causes of the pain or lack of function (rather than just addressing the site of the condition), and from that, to formulate a treatment plan that will achieve the best outcome.
Osteopaths frequently work alongside other health professionals, such as GPs, nurses and midwives as well as alternative medical practitioners. Osteopathy works well to complement other medical interventions including surgery and prescribed medication.
The National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) advises that GPs can safely refer patients to an osteopath for treatment. Osteopathy is available on the NHS in some areas
Osteopathy has been known to treat and/or help the symptoms of the following conditions…